The Burning Earth: A History Sunil Amrith W. W. Norton (2024)
In the 1620s, King Charles I of England commissioned a Dutch water engineer, Cornelius Vermuyden, to drain the flat fenlands of East Anglia, which he considered a desolate wasteland. Locals were outraged. These wetlands, writes historian Sunil Amrith in The Burning Earth, “sustained a richness of human and more-than-human life that was now in danger”. As a pamphleteer at the time declared, many thousands of cottagers lived by harvesting “reeds, fodder, thacks, turves, flaggs, hassocks, segg” and “many other fenn commodytyes”.
How the peanut trade prolonged slavery
Locals, dubbed the Fen Tigers, smashed the dams, dykes and sluice gates that had been installed to divert rivers. But England’s political elite were determined to see nature “bound into service”. The marshes were ultimately drained and the land repurposed for agriculture, with the benefits accruing to rich landowners. Now known as the bread-basket of Britain, this once biodiverse wetland is at perpetual risk of flooding.
This pattern of conquest and carnage — pitting rich against poor, colonialist against indigenous, control of nature against the flourishing of the wild — has, tragically, been repeated countless times throughout history and across the globe. Amrith narrates this sorry (and sometimes inspiring) saga with flair, in his epic exploration of human innovation and destruction.
The fenfolk of East Anglia, he notes, were not the first to lose their livelihoods and wild land to the rich — and not the last to fight back. People with power and privilege conquered the world with machinery and lethal weapons, but the poor and powerless persevere. Indigenous peoples of Brazil, Indonesia and India continue to fight corporations that encroach on their pristine rainforests, just as Fen Tigers fought for their marshlands. It is these overlooked environmental and political conflicts on which Amrith centres his narrative.
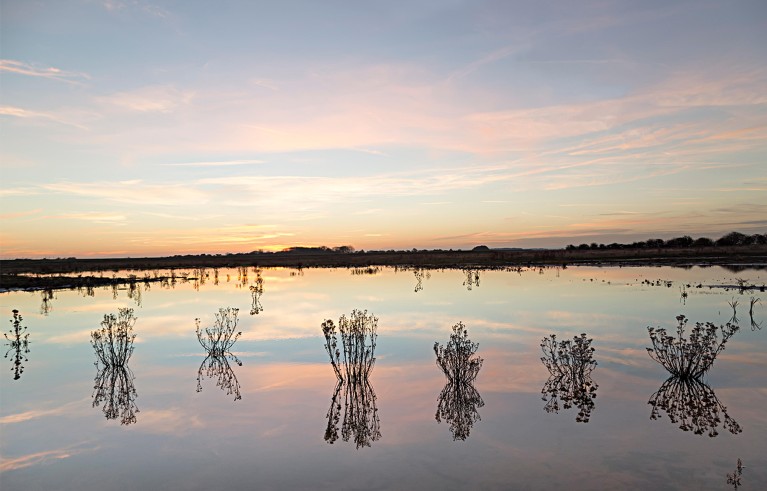

The fenlands of eastern England have been at constant risk of flooding since they were repurposed for agriculture.Credit: Chris Howes/Wild Places Photography/Alamy
Bloody commerce
For 600 years, many of these conflicts have revolved around the pursuit of luxuries. When Portuguese ships reached the North Atlantic island of Madeira in 1426, the colonists set fire to most of its forests, and later enslaved Indigenous Guanches from the nearby Canary Islands to clear the ground for sugar cultivation. In the 1470s, the Portuguese reached the coast of Ghana. In Elmina, they built a fortress that thrived as a centre first for trade in gold, ivory and peppers, and later for “the bloody Atlantic commerce in enslaved human beings”.
The climate crisis is solvable, but human rights must trump profits
At every stage, European colonists spread death and environmental destruction. In sixteenth-century Peru, Spaniards kidnapped Indigenous people and forced them to mine a mineral source of mercury called cinnabar — used to extract silver from ore. Toxic vapours from the cinnabar refineries poisoned water, mammals, fish and the shackled humans toiling at “the mine of death” at Huancavelica. As Amrith quotes one report of the time: “there used to be in this mountain”, it laments, “deer with antlers, and now not even grass is found”. Today, mercury still seeps from roads and houses made with contaminated bricks.
Rebellion and retaliation
But everywhere that people were enslaved, significant numbers rebelled. In Palmares, Brazil, a 10,000–20,000-strong quilombo, or community of once-enslaved fugitives, formed a self-governing society. Most residents, who survived on subsistence agriculture and trade, had roots in Angola and Congo, but some were Indigenous Brazilians, Jews and Muslims. Together, they held off attacks by Dutch and Portuguese militaries for almost a century, before the quilombo was conquered in 1694.
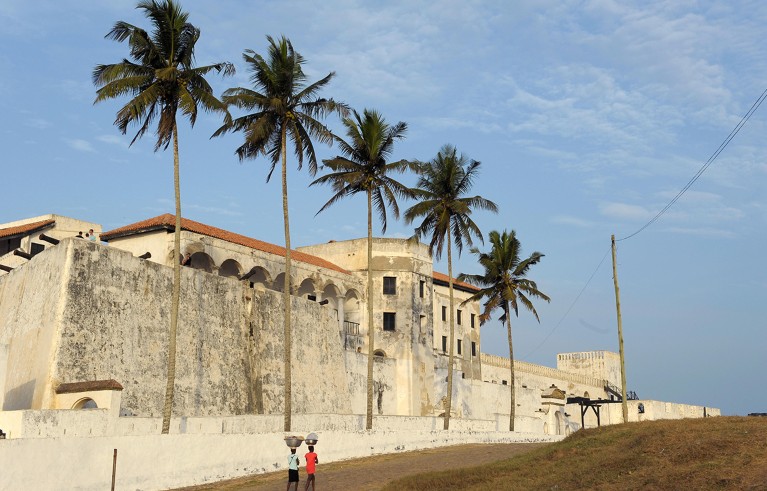

A fortress built in Elmina, Ghana, was used to hold enslaved people captive.Credit: Chuck Bigger/Alamy
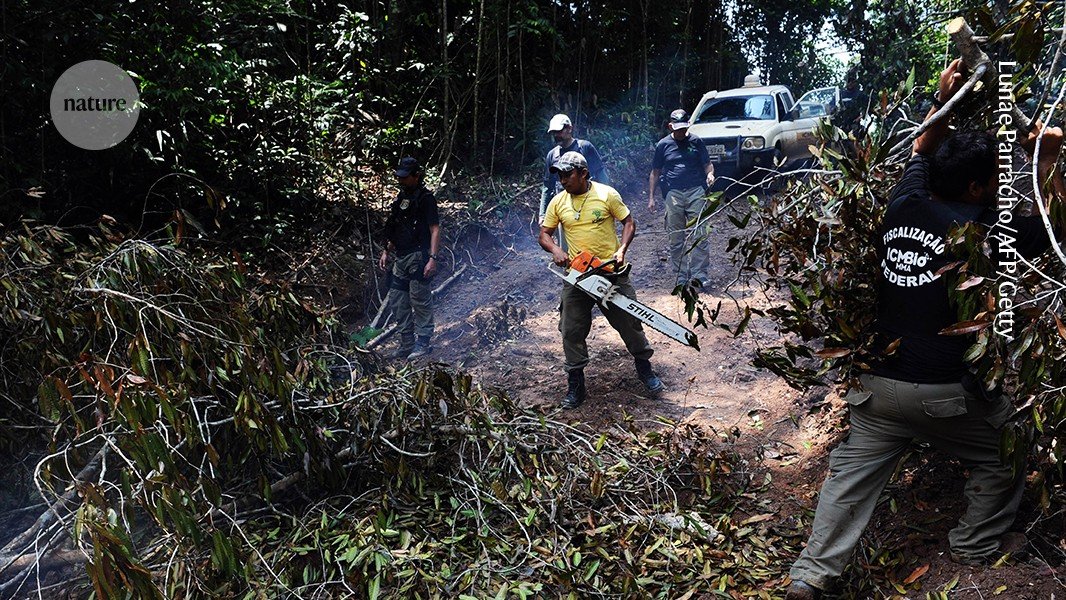
Conflicts over land and nature continue today. For centuries, Indigenous peoples in rainforests grew food, including fruit and nut trees, for their own needs; as they moved to new areas, the forests rebounded. By the 1980s, however, a contagion of chainsaws and burning had led to the loss of an area of Amazonian and southeast Asian rainforest equivalent to half the size of India. In Brazil, labour leader and conservationist Chico Mendes led the fight to establish forest reserves inhabited and managed by locals. In 1990, the state of Acre created the first such zone: the 500,000-hectare Chico Mendes Extractive Reserve. But Mendes himself had been shot dead in front of his house in Xapuri in 1988, allegedly by gunmen hired by local landowning ranchers.
In a similar grievous tale in Nigeria, environmental activist Ken Saro-Wiwa founded the Movement for the Survival of the Ogoni People, rallying 300,000 in 1993 to protest against rampant oil pollution by the energy company Shell, which had left the landscape a “desolate expanse of blackened crust”. Saro-Wiwa and eight other Ogoni leaders were imprisoned and hanged by Nigeria’s military government in 1995.
Ongoing battle
Development isn’t entirely bad, as Amrith stresses. Rates of death from infectious diseases have fallen drastically around the world since the start of the twentieth century, thanks to sanitation, vaccines and antibiotics. The Green Revolution — a period of rapid development of high-yield, disease-resistant wheat and rice varieties — led to tremendous booms in crop production. Between 1961 and 2014, production of cereal crops increased by 280% worldwide.
But the Green Revolution had unintended impacts. Petrochemicals furnished the pesticides and fertilizers on which high-yield seeds depended. Diesel powered the groundwater pumps that irrigated the harvests, and pesticides permeated and poisoned the soil. In India, the revolution also perpetuated inequality between farmers who had access to transport, water and money, and “those with land too measly, too stony, too unyielding to accept new seeds”. Thousands of farmers in India die by suicide every year, faced with debt to pay for seeds and fertilizers, amid heatwaves and drought caused by climate change.
How white supremacy became a global health problem
If there’s cause for hope, it comes from those who continue to fight for environmental justice, often from the margins. In 2006, in West Timor, Indonesia, 150 women surrounded a marble mine on Mount Mutis, protesting against the destruction of eucalyptus forests and waterways on which they depended. A few years later, mining there ceased.
And since the late 1990s in Bogotá, Colombia, 44,000 square kilometres of road have been transformed for pedestrian use, and an electrified bus network has been introduced. Five hundred kilometres of protected bicycle lanes, championed by civil-society group the Green City, intersect with the bus network.
“More and more people are challenging the self-destructive folly that captured the imagination of the powerful and privileged for two hundred years,” Amrith writes. Almost 2,000 environmental activists — one-third of them from Indigenous communities — have been murdered around the world in the past decade. Yet powerful movements, especially of young people, continue to fight for Earth’s future.
For these brave and unwavering humans, we can be grateful.